Redis Connection Refused Mac
- Redis Show Connections
- Redis Connection Refused Mac Catalina
- Redis Connection Refused Mac Os
- Mac Redis Server
- Redis Connection Exception
Redis is a very popular data store used across all kinds of web apps it’s supported natively by Mac and Linux operating systems. Heck, you can even use Docker to run Redis. The purpose of this guide is to setup Redis so we can use in our Python applications including Django, Flask, Fastapi, Celery, and pure python apps. Connection Refused error in Terminal Your server’s SSH daemon may be down for a wide variety of reasons, including unexpected traffic spikes, resource outages, or even a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack. Redis is an open source (BSD licensed), in-memory data structure store, used as a database, cache and message broker. Get Started with Redis and understand the basic knowledges of Redis. Connect to the instance using SSH. Method 2: Run the AWSSupport-TroubleshootSSH automation document. AWSSupport-TroubleshootSSH automation document installs the Amazon EC2Rescue tool on the instance. Then this tool checks for and corrects some issues that cause remote connection errors when connecting to a Linux machine through SSH.
The CLIENT LIST command returns information and statistics about the client connections server in a mostly human readable format.
You can use one of the optional subcommands to filter the list. The TYPE type subcommand filters the list by clients' type, where type is one of normal, master, replica, and pubsub. Note that clients blocked by the MONITOR command belong to the normal class.
The ID filter only returns entries for clients with IDs matching the client-id arguments.
*Return value
Bulk string reply: a unique string, formatted as follows:
- One client connection per line (separated by LF)
- Each line is composed of a succession of
property=valuefields separated by a space character.
Here is the meaning of the fields:
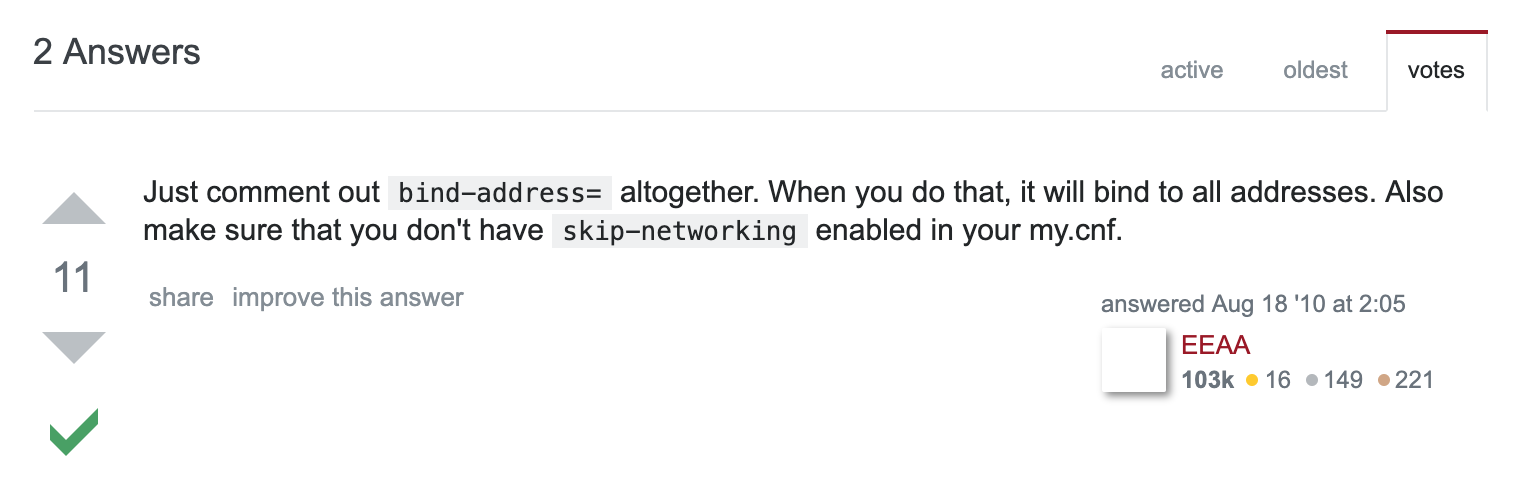
id: an unique 64-bit client ID.name: the name set by the client with CLIENT SETNAMEaddr: address/port of the clientladdr: address/port of local address client connected to (bind address)fd: file descriptor corresponding to the socketage: total duration of the connection in secondsidle: idle time of the connection in secondsflags: client flags (see below)db: current database IDsub: number of channel subscriptionspsub: number of pattern matching subscriptionsmulti: number of commands in a MULTI/EXEC contextqbuf: query buffer length (0 means no query pending)qbuf-free: free space of the query buffer (0 means the buffer is full)obl: output buffer lengtholl: output list length (replies are queued in this list when the buffer is full)omem: output buffer memory usageevents: file descriptor events (see below)cmd: last command playedargv-mem: incomplete arguments for the next command (already extracted from query buffer)tot-mem: total memory consumed by this client in its various buffersredir: client id of current client tracking redirectionuser: the authenticated username of the client
The client flags can be a combination of:
Redis Show Connections
The file descriptor events can be:
*Notes
New fields are regularly added for debugging purpose. Some could be removed in the future. A version safe Redis client using this command should parse the output accordingly (i.e. handling gracefully missing fields, skipping unknown fields).
Redis Connection Refused Mac Catalina
*History
>= 2.8.12: Added unique clientidfield.>= 5.0: Added optional TYPE filter.>= 6.2: Addedladdrfield and the optionalIDfilter.
Related commands
I'm receiving 'Connection refused' or 'Connection timed out' errors when trying to connect to my Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance using SSH. How do I resolve this?
Short description
Error message: 'Error connecting to [instance], reason: Connection timed out: connect' refers to issues with connectivity to the instance, meaning the request fails to reach the instance and times out. This might happen if SSH isn't running on the instance or if a firewall is blocking access.
Error message: 'ssh: connect to host ec2-X-X-X-X.compute-1.amazonaws.com port 22: Connection refused' indicates that the instance refused the connection or the SSH service daemon isn't running. This error might also occur if a firewall is rejecting access to the instance.
Resolution
Verify that there isn't a firewall blocking the connection, that the SSH service is running on the instance, and that SSH tcp port 22 is in the listening state.
There are three methods for performing these tasks:
Method 1: Use AWS Systems Manager Session Manager
Note: Download jab tak hai jaan full movie in torrent. Installation of the SSM Agent is required to use this method. For more information on Session Manager and a complete list of prerequisites, see Setting up Session Manager.
1. Open the AWS Systems Manager console.
2. Start a session.
3. To disable firewalls and restart the SSH service, run the following commands.
Note: The preceding command flushes all main iptables rules, not just for port 22. After you regain access to your instance, review your firewall configuration (for example, ufw, firewalld, iptables).
4. Verify that the SSH tcp port (22) is in a listening state.
5. Terminate the session.
6. Connect to the instance using SSH.
Method 2: Run the AWSSupport-TroubleshootSSH automation document
AWSSupport-TroubleshootSSH automation document installs the Amazon EC2Rescue tool on the instance. Then this tool checks for and corrects some issues that cause remote connection errors when connecting to a Linux machine through SSH. For more information, see How can I use the AWSSupport-TroubleshootSSH Automation workflow to troubleshoot SSH connection issues?
Method 3: Use a user data script
Important
- This procedure requires a stop and start of your EC2 instance. Be aware that if your instance is instance store-backed or has instance store volumes containing data, the data is lost when the instance is stopped. For more information, see Determining the root device type of your instance.
- If your instance is part of an Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling group, or if your instance is launched by services that use AWS Auto Scaling, such as Amazon EMR, AWS CloudFormation, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and so on, then stopping the instance could terminate the instance. Instance termination in this scenario depends on the instance scale-in protection settings for your Auto Scaling group. If your instance is part of an Auto Scaling group, then temporarily remove the instance from the Auto Scaling group before starting the resolution steps.
- Stopping and starting the instance changes the public IP address of your instance. It's a best practice to use an Elastic IP address instead of a public IP address when routing external traffic to your instance.
1. View the EC2 instance console logs. The following entry appears in the EC2 instance console logs if ufw is enabled.
2. Open the Amazon EC2 console.
3. Choose Instances from the navigation pane, and then select the instance you're trying to connect to.
4. Stop the instance.
5. Choose Actions, Instance Settings, View/Change User Data.
6. Copy the following user data script into the View/Change User Data dialog box, and then choose Save.
Note: The preceding command flushes all main iptables rules, not just for port 22. After you regain access to the instance, review your firewall configuration (for example, ufw, firewalld, iptables).
Redis Connection Refused Mac Os
7. Connect to the instance using SSH.
8. The preceding user data script is set to run on every reboot of the instance. After regaining access to your instance, remove the user data script.
To remove user data:
Mac Redis Server

1. Complete steps 1–4 in the Method 3: Use a user data script section.
2. Delete the user data script in the View/Change User Data dialogue box.